Introduction
Research and understanding in the field of breast cancer have focused on the complex relationship between genetics and the disease’s expression. We take a deep dive into the fascinating relationship between BRCA gene mutations and breast cancer in this blog. In addition to this investigation, we will examine the value of genetic testing and counselling, the influence of family history on the likelihood of developing breast cancer, and the variety of preventative strategies designed for high-risk individuals.
BRCA Gene Mutations and Breast Cancer
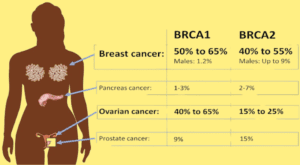
The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are the primary molecular factors influencing the risk of breast cancer. These genes are essential for preventing aberrant cell growth and preserving genetic integrity, but mutations in them can dramatically increase the risk of ovarian and breast cancer. For those who have mutations in the BRCA gene, their risk of developing breast cancer is significantly increased in comparison to those who do not have these mutations. The identification of these mutations emphasises how crucial it is to comprehend the genetic foundations of breast cancer.
Genetic Testing and Counseling
Genetic testing emerges as a beacon of clarity in the journey of individuals grappling with the specter of breast cancer. This process not only identifies BRCA gene mutations but also provides a nuanced understanding of one’s genetic landscape. Genetic counseling, an inseparable companion to testing, plays a pivotal role in ensuring a comprehensive comprehension of results, potential risks, and available preventive measures. Armed with this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions about their health, fostering a sense of empowerment and control.
Family History and Breast Cancer Risk
There are hints in the family tapestry that could have a big influence on a person’s risk of breast cancer. Strong family history, particularly early-life occurrences of breast cancer, may be suggestive of a higher genetic susceptibility. This insight becomes a critical factor to take into account, leading people to get tested for genetics in order to determine their personal risk. Knowing one’s family history turns into an effective tool that lets medical practitioners customise screening and preventive plans according to family dynamics.
Preventive Measures for High-Risk Individuals
A range of preventive strategies become available for people who have both a familial history of breast cancer and BRCA gene mutations. As steadfast protectors, preventive procedures such as mastectomy or oophorectomy greatly lower the incidence of ovarian and breast malignancies. At the same time, it is critical to embrace surveillance with vigilance through routine screens and imaging tests. These tests offer opportunities for early diagnosis, which can help minimise the impact of probable malignancies.
Beyond surgery, risk-reduction drugs, lifestyle changes, and individualised therapy regimens are all part of the preventative toolbox. People who are considered high risk can develop a plan that balances risk reduction with a focus on general well-being by arranging a symphony of techniques.
Navigating Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a proactive and health-conscious lifestyle is crucial in reducing the risk of breast cancer, even in the absence of medical therapies. Overall wellbeing is influenced by regular exercise, a diet high in fruits and vegetables, abstaining from tobacco, and moderation in alcohol use. These lifestyle decisions work in concert with medicinal therapies to provide a holistic strategy for controlling and reducing the hereditary risk factors linked to breast cancer.
Ongoing Research and Future Prospects
The field of breast cancer genetics is active, with new discoveries being made all the time. Targeted therapies and more accurate risk assessments are made possible by advances in genomics and emerging technologies. It is imperative that those navigating the complexity of hereditary predisposition to breast cancer stay up to date on these findings. In order to keep ahead of the rapidly changing area of breast cancer research, proactive approaches to ongoing research are necessary to enable patients and healthcare professionals to make well-informed decisions about genetic testing, counselling, and preventive strategies.
Support Networks and Advocacy
It can be emotionally taxing to live with the knowledge of a hereditary propensity to breast cancer. Creating and participating in advocacy and support organisations gives people a sense of belonging and common experiences. These platforms include tools, emotional support, and up-to-date research and treatment information. Engaging in advocacy activities on a regular basis helps to progress research and care for breast cancer while also decreasing stigma.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a multifaceted approach is necessary to navigate the complex relationship between BRCA gene mutations and breast cancer. People can walk this journey with resilience and empowerment, from the molecular complexities of genetic mutations to the proactive adoption of preventive measures, lifestyle choices, continuous research, and support networks. In the continuous fight against this common and profoundly damaging illness, staying informed and taking preventative measures is crucial as research into the genetic complexity of breast cancer progresses.